A simplified guide to heat treating tool steels when we consider that the greater overall costs of most tools and dies are incurred prior to heat treatment and further that proper heat treatment is critical to the successful application of tooling this so called hardening process is placed in it s proper perspective of importance.
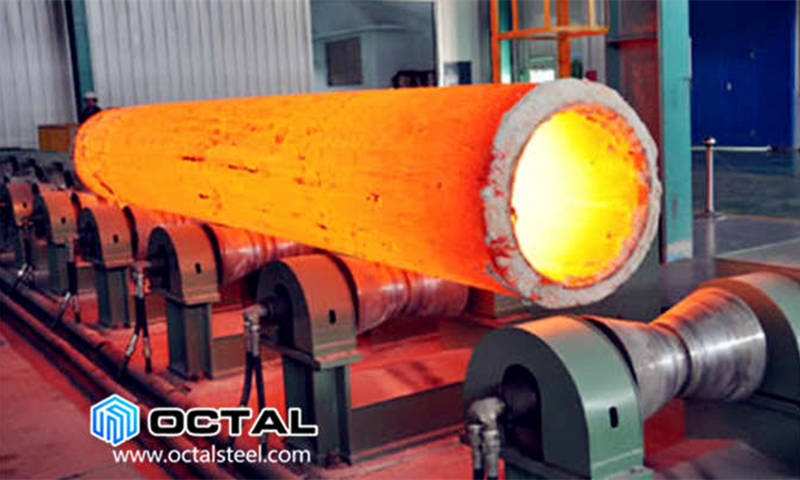
Heat treatment procedure for steel quenching.
Quenching rapid cooling up below gamma alpha.
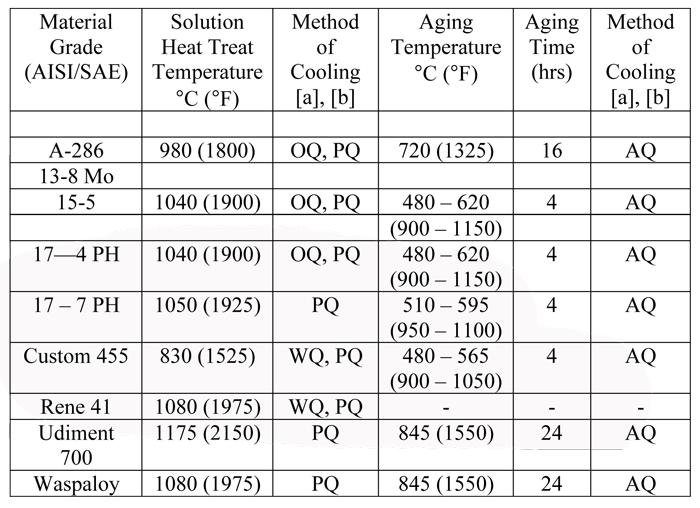
The steel has a high chromium content 11 to 13 percent and relatively high amounts of molybdenum 7 to 1 2 percent vanadium 1 1 percent cobalt 1 percent and other elements.
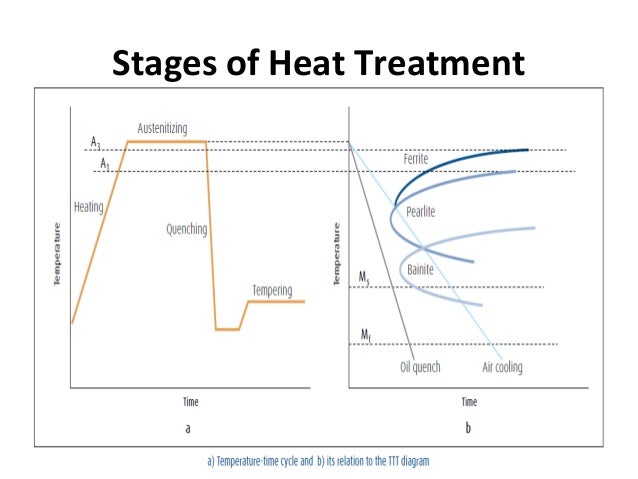
Austenitizing is the first step in most of the heat treatments for steel and cast irons.
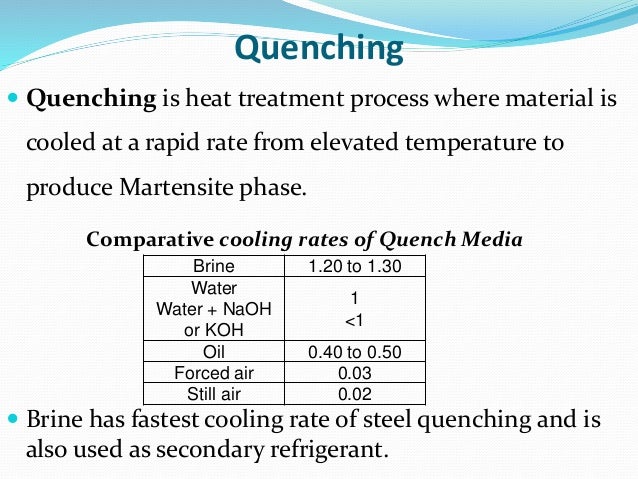
Quickly remove the steel from the furnace plunge it into a large container of water at room temperature and stir vigorously.
Purpose of heat treatment of steel.
This complex mixture makes proper heat treatment of aisi d2 more complex than the heat treatment of other simple and tool steels.
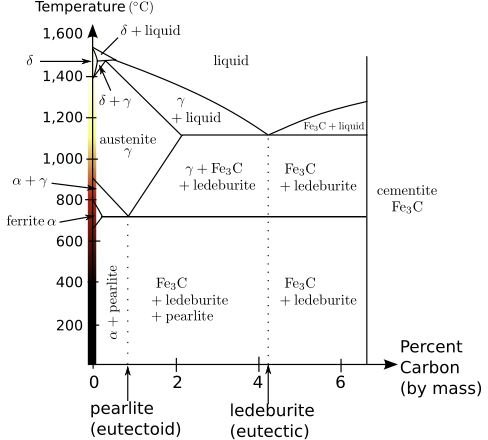
Face centered cubic phase of iron or steel.
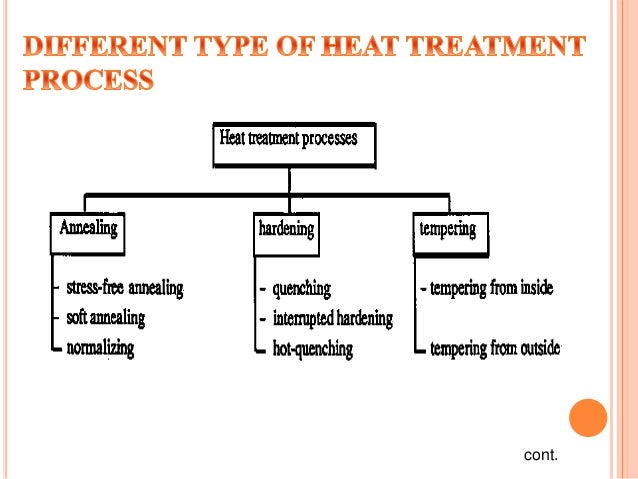
Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the steel is heated to about 50 degree celsius above the upper critical temperature followed by air cooling.
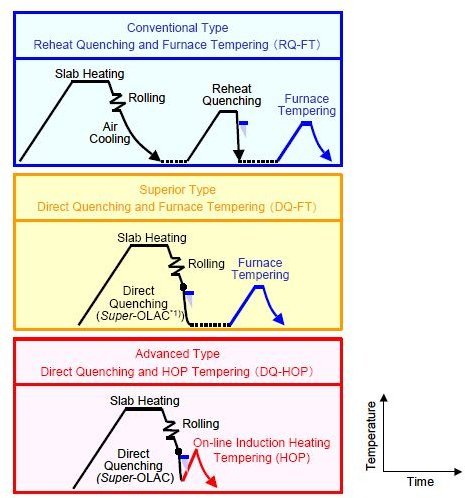
Conventional heat treatment procedures for producing martensitic steels generally involve continuous and rapid cooling of an austenitized specimen in some type of quenching medium such as water oil or air.
Describe the proper heat treating procedures for other tool steels.
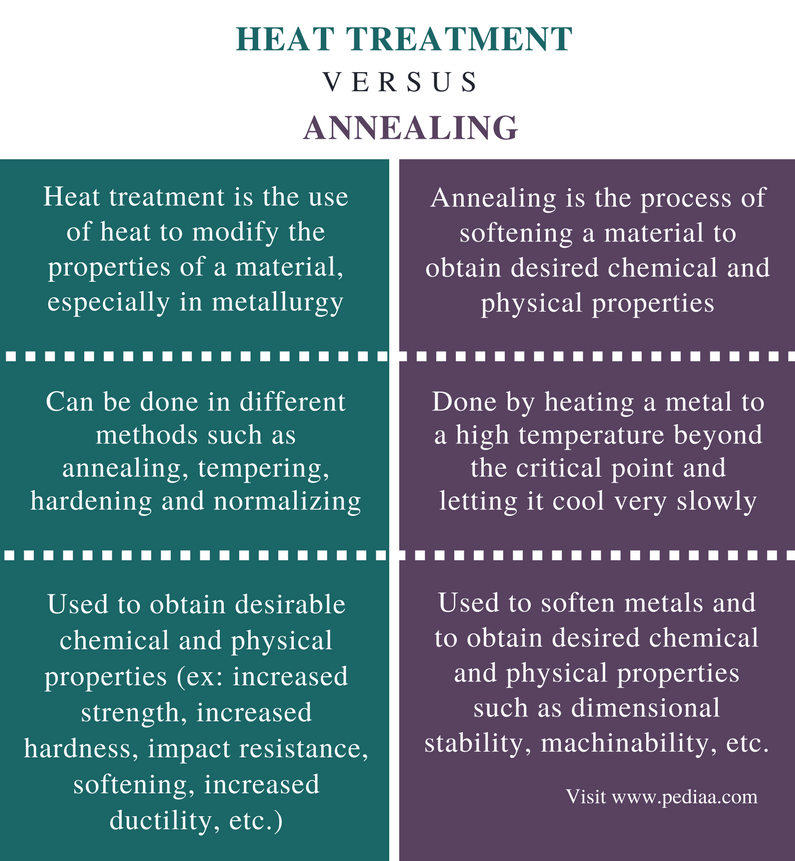
A heat treatment used to produce a soft coarse pearlite in a steel by austenitizing then furnace cooling.
This results in a softer state which will be lesser soft than that produced by annealing.
Quensching and tempering can be divided into three basic steps.
Temperature where homogeneous austenite can form.
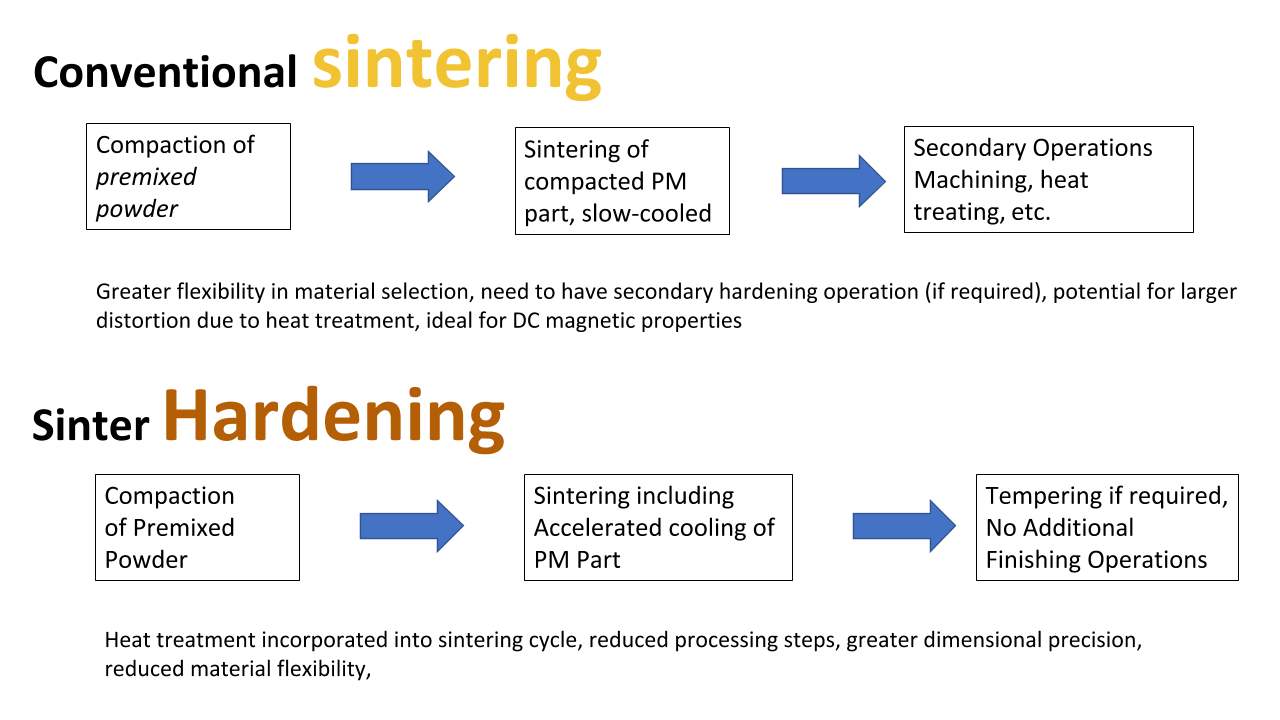
Heat treating or heat treatment is a group of industrial thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material the most common application is metallurgical heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials such as glass heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling normally to extreme temperatures.
It does this by reducing the window of time during which these undesired reactions are both thermodynamically favorable and kinetically.
The part is taken out and it does not require any quenching or further heat treatment.
Austenitizing heating to above the gsk line into the austenite region.
The properties of a steel that has been quenched and then tempered depends largely on the rate of cooling and tempering times and.
In materials science quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water oil or air to obtain certain material properties a type of heat treating quenching prevents undesired low temperature processes such as phase transformations from occurring.
The steel after being quenched in the hardening process is reheated to a temperature slightly above the temperature range at which it is to be used but below the lower critical temperature.